How healthcare organizations can harness the power of data to achieve a sustainable business advantage
In a recent study from Forrester, 90% of respondents acknowledged that their business’s overall success relies on consistent, accurate, and fast access to data and insights.1
Using integrated cloud-based data to drive foundational enterprise change
In healthcare, the volume of data is growing exponentially, yet for many organizations, the ability to extract operational value from that data is lagging behind other more data-led industries. There’s a big opportunity in harnessing the power of data to achieve sustainable data-led business advantage and value creation in healthcare, but without the right questions, approaches, and technology, data can’t be leveraged to its full capacity. Lagging behind can have a downstream effect in several key areas of business, including missed opportunities in digital transformation, and the ability to optimize clinical and non-clinical operations as well as the patient or member experience.
In this white paper, we‘ll discuss how healthcare organizations can harness the power of data to achieve a sustainable business advantage, including improved health outcomes, financial performance, and expanded market access. You’ll discover the steps needed to turn your data into a trusted, strategic asset by understanding the building blocks of dataled value creation, cloud-enabled solutions, and enterprise architecture.
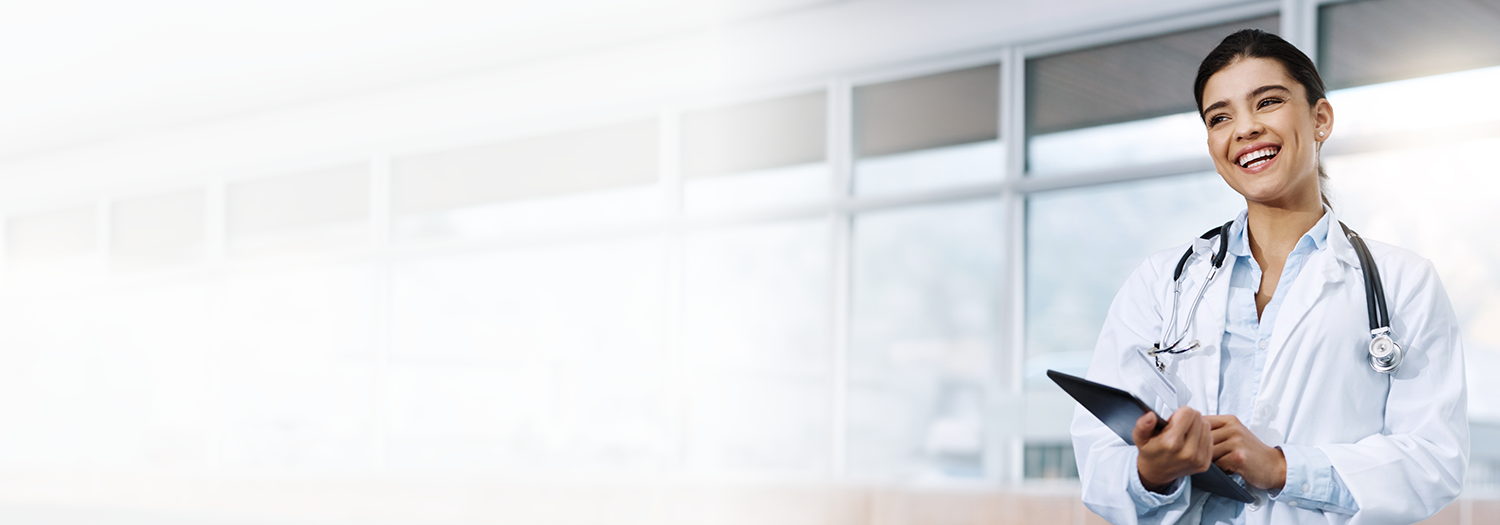
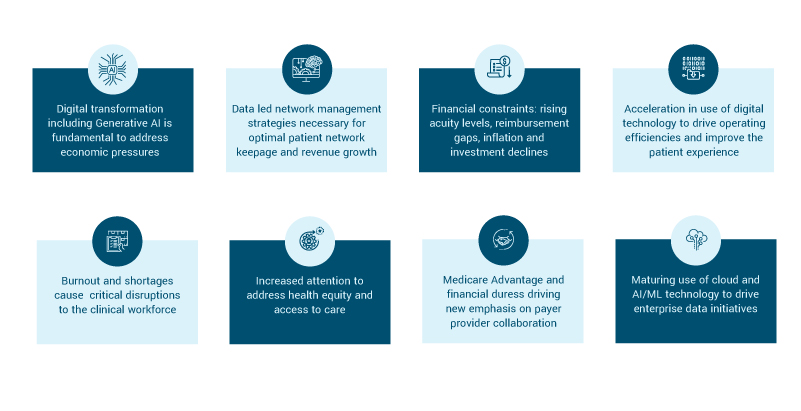
Key market challenges and technology trends for data-led healthcare organizations
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and generative AI are particularly relevant at this point in time. According to a paper recently published by the National Bureau of Economic Research, a wider adoption of AI could lead to potential cost savings of $200 billion to $360 billion annually in US healthcare spending (or 5% to 10% of the total costs) within the next five years.
In terms of generative AI specifically, there is tremendous potential in combining the power of Large Language Models with other technology, such as Natural Language Processing to automate what are critical, but often manual processes in healthcare, such as physician transcription. With physician burnout and shortages causing critical disruptions to the clinical workforce, organizations are also looking to AI to see how it may meaningfully drive efficiencies in the processes surrounding Electronic Health Records, which currently see many physicians spending evenings and weekends doing paperwork. AI has the potential here to be transformative, acting as a real catalyst for change.
There is also significant potential to use technology to transform the patient experience. While technology has the potential to solve many complex clinical problems, where most healthcare organizations are seeing more value for patients is in using digital tools to support operating efficiencies to improve the patient and member experience.
Cloud technology has also really helped healthcare organizations to bring data management to another level of scale and efficiency, and it will continue to be a critical foundational component as they go forward in terms of really unlocking the power of their data. The starting point is shifting current data assets and applications to the cloud, before looking to optimize the use of cloud-native tooling.
While the cloud is not a magic bullet, ultimately, a well-established cloud-based architecture can help healthcare organizations to bring together operational and clinical data to drive enterprise data initiatives. Many still face a cloud learning curve, however, its potential to give us a 360-degree view of patient data while driving better analytics and reporting is a trend that will continue.
Market challenges and trends
Harnessing the power of data to achieve sustainable business outcomes
With well-orchestrated execution, an enterprise data strategy can result in improved health outcomes and financial performance, as well as expanded market access. However, becoming data-led requires striking a fine balance in order to achieve demonstrable outcomes. Data must be used to generate intelligence and prompt change, and to do this, it has to be analytically usable. Simply having data stored in one location will not produce insights; the ability to organize it, apply enrichments to it, create visualization from it, and make it easily consumable is still essential.
True digital transformation in healthcare is really about embedding intelligence in physician and hospital workflows to enable decision-making, both from an administrative and clinical perspective. While this will mean automating some processes in full, it will also mean incorporating digital capabilities intelligently while keeping humans in the loop for processes that require human interaction.
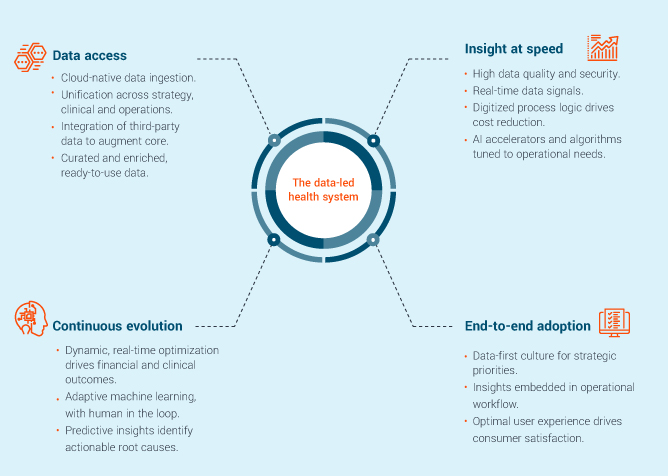
We believe that successful data-led healthcare organizations are driven by four tenets that must be addressed in order to unlock the power of their data:
- Data access: Organizations need the right data. A cloud environment can be an enabler in terms of making that data available.
- Insight at speed: Being able to generate insights at speed is critically important in order to drive cost reduction and serve operational needs in an efficient, competitive manner.
- Continuous Evolution: Insights need to be actionable: the ability to create repeatable, scalable insights is a true differentiator. We’re seeing the acceleration in AI and machine learning capabilities, and that’s going to continue. The quality of capabilities of advanced models will continue to evolve, and Large Language Models that are trained and continue to evolve over time are a hallmark of where we are in terms of analytical tools.
- End-to-end adoption: Data literacy support leaders must understand that data-driven insights need to become part of the culture of a health system or other healthcare organization. Many may have achieved data access at speed, and others may have a mature set of analytical capabilities. However, if the entire organization is not using data-based insights to make decisions, it is unlikely to achieve differentiated performance in the market.
Explore the 4 tenets
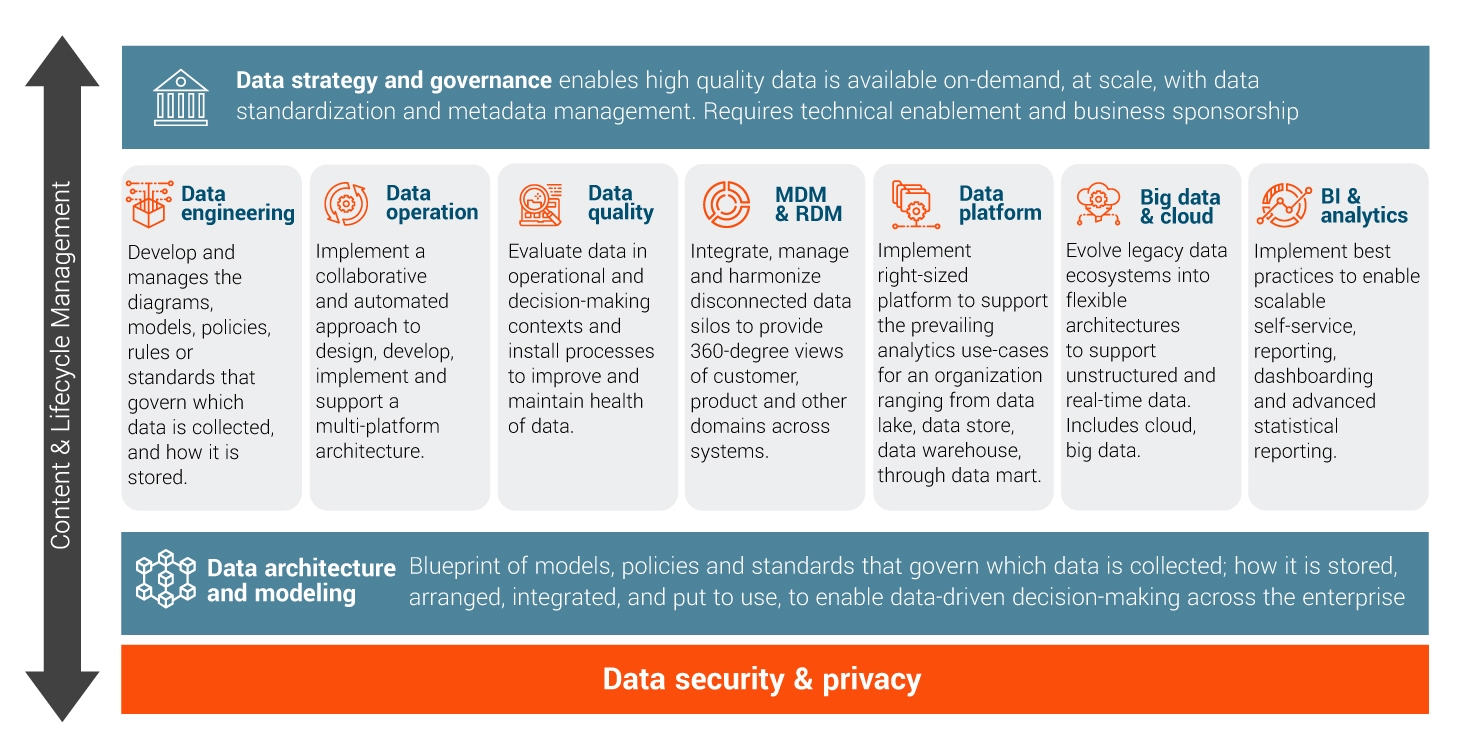
Key underlying functions in a data-led infrastructure
Large cloud vendors can provide the building blocks in the systems and infrastructure that can then be tailored to support specific data needs for health systems and health plans. However, healthcare leaders will still have to organize, curate and develop their own data in order to enable their own business priorities.
Often, when organizations are responsible for data governance and data sponsorship there this can lead to gaps and a disconnect between the technical management of data and the needs of the business. To resolve this, a comprehensive data strategy and Data Governance Program is a common solution, and it is usually sponsored through a combination of key business leaders and IT leaders. This ensures that the investments that are made from a data management perspective, and are directly related to business priorities designed to yield specific business results.
This is also where data engineering becomes critically important, as it gives organizations the ability to really move data right at scale, organize data and manage data. As an operation, data management needs to be approached in a way so that investments are made as a data structure evolves, and so that the value and potential of the data grows over time - as opposed to having a fragmented development infrastructure that leads to technical debt or an infrastructure that becomes increasingly heavy and expensive to manage. Having a plan with thoughtful management and execution becomes part of the data footprint of an organization as it grows.
Enterprise data strategy and delivery enables business priorities
How can data add value to your organization?
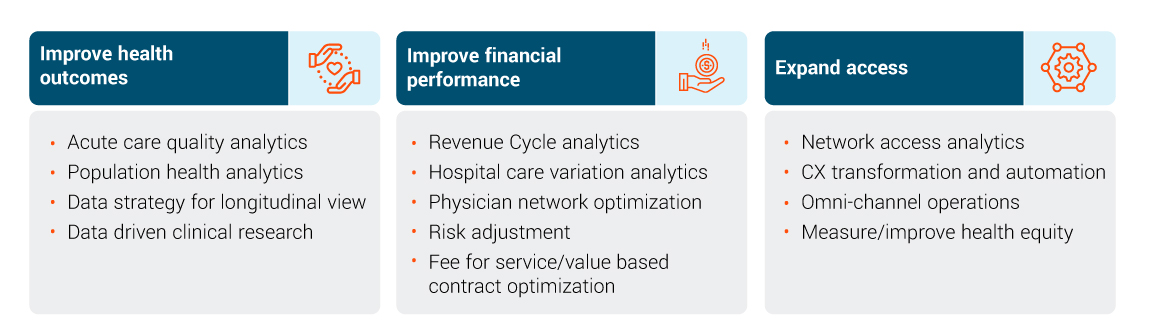
Critical business outcomes of a high-value data infrastructure
Ultimately, a good enterprise data strategy and delivery can enable business priorities and key differentiators, including improved health outcomes, improved financial performance, and expanded access.
For example, the advancements in electronic health records can provide a clinical operational mechanism and access to a more comprehensive view of a patient for more informed decision making and better health outcomes.
From a financial perspective, organizations are also seeing success in using data to drive better revenue cycles, care variations, and optimization the physician network. In expanding access to data analytics, many organizations are looking beyond the data that’s contained in an EHR and making use of other sources of information related to consumer buying patterns and behaviors. They are looking to examples provided in other industries that have evolved with their use of other data sources to think about customers more holistically and multi-dimensionally. They are looking to incorporate these same types of information to supplement the richness of the clinical data that exists today to create outreach to patients who may be in need of specific services.
These are just a few examples of the improved outcomes we’re seeing with a data-led approach, as well as opportunities where healthcare organizations may see success with evolved data use in the near future. In the next section, we’ll review a case study that outlines how one healthcare organization is making the most of data-led opportunities to drive enterprise change.
Saving physician group/ACO millions with AI-driven risk adjustment to reduce errors and improve documentation
The challenge: EXL was brought in to help this provider solve inaccuracies in its Hierarchical Condition Category (HCC) coding, as well as inefficiencies and inaccuracies in its documentation process. The provider was at risk for higher revenue shortfall and had increased susceptibility to regulatory scrutiny and penalties.
The solution:
- EXL reviewed the provider’s electronic medical records (EMR), performing coding audits and identifying document gaps in order to recommend corrections for the EMR documentation.
- The group’s data was reviewed in order to understand where documentation gaps existed, and where the risk score could be improved. A team of high-performing HCC coders were provided to improve the risk adjustment score factor, and partnered with the provider’s team in order to ensure they were fully educated on the new process.
- The team was also able to leverage data in the medical records order to determine whether chronic or other potential conditions should be highlighted to physicians, integrating a predictive element into helping providers to find better care.
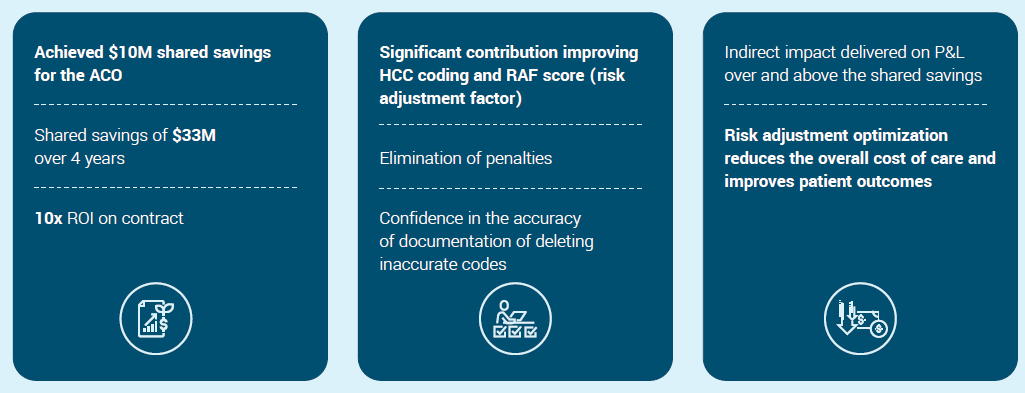
The value impact:
The future of data in driving value in healthcare
Every healthcare organization sits on a different point on the data and analytics maturity curve, but many of the fundamentals required for success remain the same. Success in driving value from healthcare data starts at having invested across the organization, including senior level decision makers and analytic and technical professionals who are committed to defining and evolving the data strategy.
In many instances, forming a steering group can be remarkably effective, and this may include a vision goal statement for your desired outcomes and priorities. As technologies such as generative AI continue to develop rapidly and introduce new opportunities, a solid vision can be helpful for capitalizing on these new opportunities, while also maintaining solid governance over the end-to-end everyday enterprise data strategy.
